 |
the Ultimate Gutter |  |
 |
 |
| Luctor et Emergo (Pump or Drawn) |
and windmills, a search for the Ultimate Gutter Dimensions..
See section below:
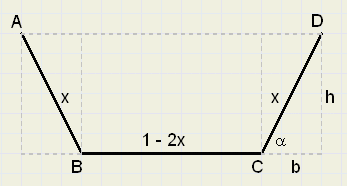 |
Variables are angle a and length x.
Question: for which values of a and x, will area ABCD have a maximum?
Two solutions are presented:
-
1. graphical (using Graphics-Explorer)
2. analytical (application of calculus)
 |
| Dutch windmill |
See picture above::
The area A is the addition of a rectangle (1-2x)h
and two triangles, together bh, so:
-
A = (1 - 2x)h + bh
-
h = x.sin(a)
b = x.cos(a)
-
A = x2.sin(a).cos(a) + (1 - 2x).x.sin(a)
A = x2.sin(a).cos(a) + x.sin(a) - 2x2.sin(a)
the Graphical solution
Graphics-Explorer uses variables x en y.
Also, constants (a,b,c) may be used in formula's.
These constants are changeble by mouseclick, graphics adjust to new values.
It's obvious to use x for a side, y for the area and a for the angle a.
Type the formula:
-
y = x^2*sin(a)*cos(a) + x*sin(a) - 2x^2*sin(a)
-
- angles: degrees instead of radians
- coordinates (0,0) left-bottom
- +/- value for constants increment: 5 (degrees)
- zoom-center at (0,0)
- x- scale (1) at right side (x < 1)
- y- scale (0.2) at top
- "Autoplot" (to make graphics adjust on constants change)
- "replace" (to enable cleanup of old graphics)
Observe maximum value of y and read values of x en a, see picure below:
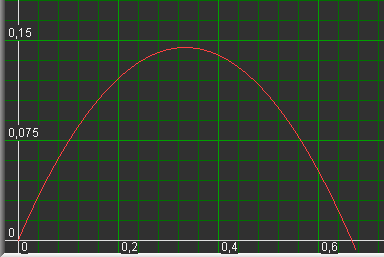 |
is near 60 degrees and bottom and sides have about equal lengths.
The analytical approach
The maximum or minimum of a function can be found by differentiation.
The derivative of a function equals 0 in this case.
There are 2 variables, x and a,
so, for a maximum of y both the derivatives of A to x as well as A to a must be 0.
Differentiation of A to x
| d A |
| d x |
2 x · cos a + 1 − 4 x = 0
2 x · cos a = 4 x − 1
cos a =
| 4 x − 1 |
| 2 x |
| d A |
| d a |
x 2 ( cos a) 2 − x 2 ( sin a) 2 + x · cos a − 2 x 2 · cos a = 0
x ( cos a) 2 − x ( sin a) 2 + cos a − 2 x · cos a = 0
x ( cos a) 2 − x + x ( cos a) 2 + cos a − 2 x · cos a = 0
2 x ( cos a) 2 + (1 − 2 x) · cos a − x = 0
-
2 x
| 2 | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| (1 − 2 x) (4 x − 1) |
| 2 x |
(4 x − 1) 2 + (1 − 2 x) (4 x − 1) − 2 x 2 = 0
16 x 2 − 8 x + 1 + 4 x − 1 − 8 x 2 + 2 x − 2 x 2 = 0
6 x 2 − 2 x = 0
x =
| 1 |
| 3 |
| = |
|
The ultimate gutter has sides with an angle of 60 degrees. Bottom and sides have equal lengths.